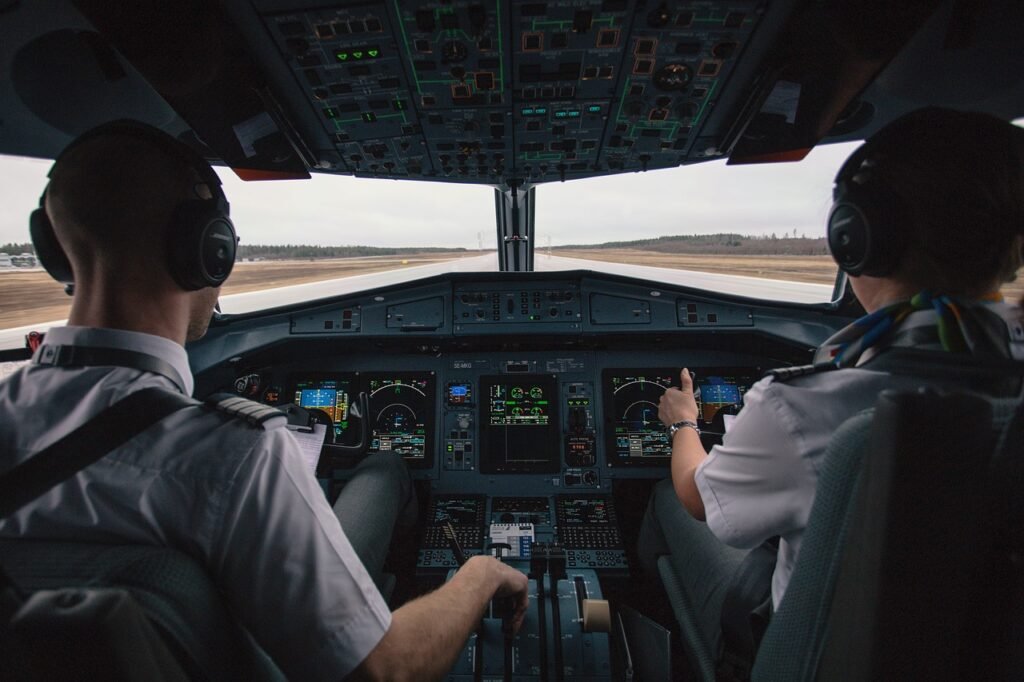
Becoming a bush pilot is a dream for many aviation enthusiasts. These pilots operate in some of the most remote and challenging environments in the world, flying into areas that commercial airliners cannot reach. Their work often involves transporting goods, people, and supplies to isolated locations or responding to emergency situations in rugged terrain. However, pursuing a career as a bush pilot requires a specific set of skills, experience, and certifications that go beyond the training of a typical commercial pilot. A question often asked by those interested in this unique career path is, how long is the training for a bush pilot?
In this article, we will explore the training required to become a bush pilot, the different steps involved, and the various factors that can influence the duration of the training process. We will also answer some frequently asked questions related to bush pilot training and career paths.
What Is a Bush Pilot?
how long is the training for a bush pilot who flies in remote and rural areas, typically using smaller aircraft that are able to land on shorter and less developed airstrips. These pilots often operate in places where commercial airlines do not go, flying into locations with minimal infrastructure or none at all. Their work includes transporting cargo, medical supplies, passengers, and conducting search and rescue missions in difficult conditions.
Key Characteristics of a Bush Pilot:
- Flying in Remote Areas: Bush pilots fly in areas with little to no developed infrastructure, such as forests, mountains, or deserts.
- Use of Smaller Aircraft: Bush pilots often fly smaller planes like Cessna 172s, Piper Cubs, or specialized bush planes designed for rough terrain and short takeoffs and landings.
- Adaptability: These pilots need to be adaptable and resourceful since they often deal with unpredictable weather, difficult terrain, and limited resources.
- Wide Range of Tasks: Bush pilots may perform tasks ranging from cargo and passenger transport to emergency medical evacuations and search and rescue missions.
The Training Process for a Bush Pilot
Becoming a bush pilot is not a single-step process. It involves several stages of training, starting with obtaining a private pilot’s license (PPL), followed by more advanced certifications and experience specific to the bush flying environment.
1. Private Pilot’s License (PPL)
The first step toward becoming a bush pilot is obtaining a private pilot’s license (PPL). This is the foundational certification for all pilots. The training for a PPL generally takes between 3 to 6 months if the pilot is flying full-time and has regular lessons.
Requirements for a PPL:
- Minimum Age: You must be at least 17 years old.
- Medical Certificate: A third-class medical certificate from an aviation medical examiner is required.
- Flight Hours: You must complete a minimum of 40 flight hours, including time spent flying with an instructor (dual flight hours) and solo flights.
- Written Exam: You must pass a written exam covering topics such as navigation, flight rules, and meteorology.
- Check Ride: You will need to successfully complete a flight test (check ride) with a certified examiner to demonstrate your skills.
2. Time-Building and Experience
Once you have your private pilot’s license, you’ll need to accumulate flight hours and experience before you can move on to more advanced certifications. This period, often referred to as time-building, can take anywhere from several months to a few years, depending on how often you fly and the type of flying you do.
How long does time-building take?
- Flight Hours: Most bush pilot training schools recommend logging anywhere from 300 to 500 flight hours before moving on to commercial certification, though some schools might require more depending on the region and type of aircraft used.
- Flight Experience: During this time, pilots often fly in various weather conditions, complete long cross-country flights, and gain exposure to different types of aircraft, including tailwheel planes, which are often preferred for bush flying.
3. Commercial Pilot’s License (CPL)
To become a bush pilot, obtaining a commercial pilot’s license (CPL) is typically required. The CPL allows pilots to fly for compensation, which is essential for most bush pilot jobs, as they will likely be paid to operate aircraft in remote areas.
The training for a CPL takes approximately 6 to 12 months, and includes both theoretical and practical components.
Requirements for a CPL:
- Flight Hours: A commercial pilot’s license generally requires a minimum of 250 flight hours, though this may vary depending on the country or aviation authority. This includes both dual and solo flight hours.
- Written Exam: The written exam for the CPL is more advanced than the PPL exam and covers topics such as aerodynamics, navigation, and flight operations.
- Flight Test: Like the PPL, a flight test or check ride is required to demonstrate proficiency in operating an aircraft.
4. Tailwheel (Taildragger) Training
Many bush pilots fly tailwheel aircraft (also known as taildraggers), which are better suited for operating on rough, short, or unimproved airstrips. These planes are often lighter, more durable, and can take off and land in shorter distances than tricycle-gear aircraft.
Tailwheel Training:
- Duration: Depending on the pilot’s experience and comfort level, tailwheel training can take anywhere from 10 to 30 hours.
- Importance for Bush Pilots: Tailwheel aircraft are ideal for the unpredictable nature of bush flying, especially when dealing with rough terrain or small, undeveloped landing strips.
5. Bush Pilot Training
Bush pilot training is highly specialized and focuses on the unique skills needed to fly in remote and often hazardous environments. This training typically includes:
- Short Takeoff and Landing (STOL): Bush pilots must be able to operate aircraft in environments with short or unimproved landing strips. They are trained in techniques for taking off and landing in a short distance.
- Weather Awareness: Pilots learn to read weather patterns and understand how different weather conditions, such as fog, wind, and thunderstorms, can impact their ability to safely operate an aircraft in remote areas.
- Navigation and Survival: Pilots are trained in flying over wilderness areas where landmarks may be scarce. They also learn survival skills in case of an emergency, such as how to find water, build a shelter, and signal for help.
- Aerial Work: Bush pilots may also be trained in specialized tasks, such as aerial firefighting, transporting cargo, or conducting medical evacuations.
Duration of Bush Pilot Training:
- Time Frame: Depending on the specific training program and the pilot’s prior experience, bush pilot training can last anywhere from 3 to 6 months. This training is often done through specialized schools or flight academies that focus on the skills needed for bush flying.
6. Additional Certifications and Experience
In addition to the basic qualifications mentioned above, many bush pilots also pursue additional certifications and endorsements, such as:
- Instrument Rating: Allows pilots to fly in conditions where visual reference to the ground is not possible, such as flying through clouds or at night.
- Type Ratings: Specialized training for flying specific types of aircraft.
- Search and Rescue (SAR) Certification: For pilots who may be called upon for rescue missions in remote or challenging conditions.
These additional certifications can add several months to the overall training timeline.
How long is the training for a bush pilot?
In total, the training to become a bush pilot can take anywhere from 1 to 2 years depending on your starting point, the amount of time you dedicate to training, and the specific requirements of the bush flying environment you are entering. This includes time spent obtaining a private pilot’s license, gaining flight experience, earning a commercial pilot’s license, and completing specialized bush pilot training.
It’s important to note that while the technical training may take a certain amount of time, the real experience and learning often come once you start working as a bush pilot. It’s during these years of practical experience that you’ll truly develop the skills necessary to handle the challenges of remote flying.
FAQs About Bush Pilot Training
Q1: Can you become a bush pilot without a commercial license?
A1: It is highly unlikely that you can become how long is the training for a bush pilot without a commercial pilot’s license. A commercial license is essential for most paid flying jobs in the bush pilot sector.
Q2: Do bush pilots need a specific type of aircraft?
A2: While many bush pilots fly tailwheel (taildragger) aircraft, they are trained to fly a variety of smaller planes. The choice of aircraft depends on the region, the terrain, and the type of work being done.
Q3: How much does bush pilot training cost?
A3: The cost of bush pilot training varies depending on the flight school and location, but it can range from $10,000 to $30,000 or more. Additional certifications and flight hours can add to the cost.
Q4: Is bush pilot training physically demanding?
A4: Yes, bush pilot training can be physically demanding. Pilots often fly in rugged conditions, dealing with extreme weather, long hours, and physically challenging environments. However, the training itself primarily focuses on technical and skill-based aspects.
Q5: What is the best way to gain experience as a bush pilot?
A5: The best way to gain experience is to work in smaller, more remote operations that provide exposure to the types of flying you’ll do as a bush pilot. Many bush pilots start with jobs in less demanding environments before moving on to more challenging locations.
Conclusion
How long is the training for a bush pilot is a rewarding and challenging career path that requires dedication, skill, and a deep love for flying in remote and often difficult conditions. The training to become a bush pilot is multifaceted and can take between 1 to 2 years, depending on the individual’s pace and prior experience. It involves obtaining a private pilot’s license, accumulating flight hours, obtaining a commercial license, and undergoing specialized bush pilot training.
For those with a passion for adventure and a desire to explore some of the most untouched parts of the world, becoming a bush pilot can be an incredibly fulfilling career. While the training process may be demanding, the payoff is a career that offers not only the thrill of flying but also the opportunity to make a real difference in the lives of people living in remote regions.